Keep a Watchful Eye on the Bridges IELTS Reading Passage with Answers
Reading Passage 1
Keep a Watchful Eye on the Bridges
A.
Most road and rail bridges are only inspected visually, if at all. Every few months, engineers have to clamber over the structure in an attempt to find problems before the bridge shows obvious signs of damage. Technologies developed at Los Alamos National Laboratory, New Mexico, and Texas A&M University may replace these surveys with microwave sensors that constantly monitor the condition of bridges.
B.
“The device uses microwaves to measure the distance between the sensor and the bridge, much like radar does,” says Albert Migliori, a Los Alamos physicist “Any load on the bridge – such as traffic induces displacements, which change that distance as the bridge moves up and down.” By monitoring these movements over several minutes, the researchers can find out how the bridge resonates. Changes in its behaviour can give an early warning of damage.
C.
The Interstate 40 bridge over the Rio Grande river in Albuquerque provided the researchers with a rare opportunity to test their ideas. Chuck Farrar, an engineer at Los Alamos, explains: “The New Mexico authorities decided to raze this bridge and replace it. We were able to mount instruments on it, test it under various load conditions and even inflict damage just before it was demolished.” In the 1960s and 1970s, 2500 similar bridges were built in the US. They have two steel girders supporting the load in each section. Highway experts know that this design is “fracture critical” because a failure in either girder would cause the bridge to fail.
D.
After setting up the microwave dish on the ground below the bridge, the Los Alamos team installed conventional accelerometers at several points along the span to measure its motion. They then tested the bridge while traffic roared across it and while subjecting it to pounding from a “shaker”, which delivered precise punches to a specific point on the road.
E.
“We then created damage that we hoped would simulate fatigue cracks that can occur in steel girders,” says Farrar. They first cut a slot about 60 centimetres long in the middle of one girder. They then extended the cut until it reached the bottom of the girder and finally they cut across the flange – the bottom of the girder’s “I” shape.
F.
The initial, crude analysis of the bridge’s behaviour, based on the frequency at which the bridge resonates, did not indicate that anything was wrong until the flange was damaged. But later the data were reanalysed with algorithms that took into account changes in the mode shapes of the structure – shapes that the structure takes on when excited at a particular frequency. These more sophisticated algorithms, which were developed by Norris Stubbs at Texas A&M University, successfully identified and located the damage caused by the initial cut.
G.
“When any structure vibrates, the energy is distributed throughout with some points not moving, while others vibrate strongly at various frequencies,” says Stubbs. “My algorithms use pattern recognition to detect changes in the distribution of this energy.” NASA already uses Stubbs’ method to check the behaviour of the body flap that slows space shuttles down after they land.
H.
A commercial system based on the Los Alamos hardware is now available, complete with the Stubbs algorithms, from the Quatro Corporation in Albuquerque for about $100,000. Tim Darling, another Los Alamos physicist working on the microwave interferometer with Migliori, says that as the electronics become cheaper, a microwave inspection system will eventually be applied to most large bridges in the US. “In a decade I would like to see a battery or solar-powered package mounted under each bridge, scanning it every day to detect changes,” he says.
Questions 1-4
Choose the correct letter out of the options, A, B, C or D.
Write your answers in boxes 1-4 on your answer sheet.
1. How did the traditional way to prevent damage to the bridges before the invention of the new monitoring system
A. Bridges have to be tested in every movement on two points.
B. Bridges have to be closely monitored by microwave devices.
C. Bridges have already been monitored by sensors.
D. Bridges have to be frequently inspected by professional workers with naked eyes.
2. How does the new microwave monitors find out the problems of bridges
A. by changeling the distance between the positions of devices
B. by controlling the traffic flow on the bridges
C. by monitoring the distance caused by traffic between two points
D. by displacement of the several critical parts in the bridges
3. Why did the expert believe there is a problem for the design called “fracture critical”
A. Engineers failed to apply the newly developed construction materials.
B. There was not enough finance to repair the bridges.
C. The supporting parts of the bridges may crack and cause the bridge to fail.
D. There were bigger traffic load conditions than the designers had anticipated.
4. The defect was not recognized by a basic method in the beginning
A. until the mid of faces of bridges has fractured.
B. until the damage appears along and down to the flanges.
C. until the points on the road have been punched.
D. until the frequency of resonates appears disordered.
Questions 5-8
Write the correct answer in boxes 5-8 on your answer sheet.
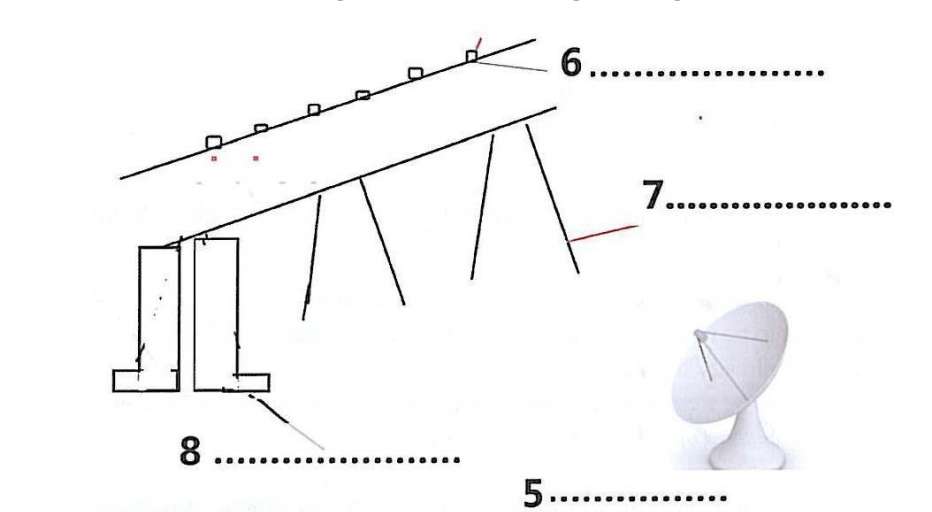
The Diagram of Monitoring a Bridge
Questions 9-13
The reading Passage has eight paragraphs, A–H.
Which paragraph contains the following information?
Write the correct letter, A-H, in boxes 9-13 on your answer sheet.
9. how is the pressure that they have many a great chance to test bridges
10. a ten-year positive change for microwave device
11. the chance they get an honourable contract
12. explanation of the mechanism for the new microwave monitoring to work
13. how the damage was deliberately created by the researchers
Additional questions for practice:
14. trying to find problems before the bridge shows obvious signs of damage.
15. the shapes that the structure takes when it enjoys a certain frequently.
16. hit it with a “shaker” at a certain point on the road.
Keep a Watchful Eye on the Bridges IELTS Reading Passage Answers
Practice with Expert IELTS Tutors Online
Apply Code "IELTSXPRESS20" To Get 20% off on IELTS Mock Test
1. D
2. C
3. C
4. B
5. microwave dish
6. accelerometers
7. steel girders
8. flange
9. C
10. H
11. G
12. B
13. E
Additional Questions’ Answers:
14. A
15. F
16. D
Keep a Watchful Eye on the Bridges IELTS Reading Answers Explanation
Question 1. How did the traditional way to prevent damage of the bridges before the invention of new monitoring system?
Answer: D) Bridges has to be frequently inspected by professional workers with naked eyes.
Supporting sentence: As the technologies were not well developed during the traditional times. Therefore, the engineers back in old system used to check & repair any damage with the available tools
Keywords: Rail bridge, engineers
Keyword Location: 1st paragraph, 1st line.
Explanation: Most road and rail bridges are only inspected visually, if at all. Every few months, engineers have to clamber over the structure in an attempt to find problems before the bridge shows obvious signs of damage.
Question 2. How do the new microwave monitors find out the problems of bridges?
Answer: C) by monitoring the distance caused by traffic between two points
Supporting sentence: By monitoring these movements for a few minutes, the researchers are able to find out how the bridge resonates. Changes in its pattern can give an early warning of damage.
Keywords: microwave, radar, sensor
Keyword Location: 2nd paragraph. 1st line.
Explanation: The device uses microwaves to measure the distance between the sensor and the bridge, much like radar does,” “Any load on the bridge – such as traffic-induced displacements.
Question 3. Why did the expert believe there is a problem for the design called “fracture critical”
Answer: C The supporting parts of the bridges may crack and cause the bridge to fail
Supporting sentence: There were steel girders supporting the load in each section. The design is “fracture critical” because a failure in either girder would cause the bridge to fail as one girder is not strong enough to bare the load of whole bridge
Keywords: Fracture, failure, girder.
Keyword Location: 3rd paragraph, last line.
Explanation: Highway experts know that this design is “fracture critical” because a failure in either girder would cause the bridge to fail.
Question 4. Defect was not recognized by a basic method in the beginning.
Answer: B until the damage appears along and down to the flanges.
Supporting sentence: It means that the early damages were not recognized in the bridge until the parts further got injured till the flanges. But later the data were reanalysed with algorithms that took into account changes in the mode shapes of the structure.
Keywords: Bridge, flange, frequency
Keyword Location: 6th paragraph, 1st line.
Explanation: The initial, crude analysis of the bridge’s behaviour, based on the frequency at which the bridge resonates, did not indicate that anything was wrong until the flange was damaged
Question 5. Something circular, appear below the bridge:
Answer: Microwave dish
Supporting sentence: Highway experts set up the microwave dish below the bridge on ground with accelerometers to measure the motion.
Keywords: Microwave, accelerometers, motion
Keyword Location: 4th paragraph, 1st line
Explanation: After setting up the microwave dish on the ground below the bridge, the Los Alamos team installed conventional accelerometers at several points along the span to measure its motion.
Question 6. Something small, appear along the bridge:
Answer: Accelerometers
Supporting sentence: The conventional accelerometers are installed to measure the motion, after which the bridge was tested when the traffic was quite high.
Keywords: Accelerometers, motion, traffic
Keyword Location: 4th paragraph, 1st line.
Explanation: After setting up the microwave dish on the ground below the bridge, the Los Alamos team installed conventional accelerometers at several points along the span to measure its motion.
Question 7. Two things under the bridge and are supporting it:
Answer: Steel Girders
Supporting sentence: The Mexico authorities decided to test the bridge under varied load conditions to see how much pressure the bridge can handle. Also, they decided to inflict damage before it was taken down. They had two steel girders supporting the load in each section
Keywords: Steel girders, bridge, damage.
Keyword Location: 3rd Paragraph, 4th line
Explanation: In the 1960s and 1970s, 2500 similar bridges were built in the US. They have two steel girders supporting the load in each section.
Question 8. Something under the bridge with a “L” (or “I”) shape:
Answer: Flange
Supporting sentence: There were damages created for simulating the cracks that were probably going to occur in steel girders. They first cut a slot about 60 centimetres long in the middle of one girder. They then extended the cut until it reached the bottom of the girder and finally they cut across the flange
Keywords: Engineers, flange, cracks
Keyword Location: 5th paragraph, last line.
Explanation: The engineers extended the cut until it reached the bottom of the girder and finally they cut across the flange – the bottom of the girder’s “I” shape.
Question 9. How is the pressure that they have many great chances to test bridges?
Answer: C
Supporting sentence: In the 1960s and 1970s, 2500 similar bridges were built in the US. They had two steel girders supporting the load of each section. Highway experts knew that this design is “fracture critical” because a failure in either girder would cause the bridge to fail.
Keywords: damage, authorities, instruments
Keyword Location: 3rd Paragraph, 3rd line
Explanation: The New Mexico authorities decided to raze this bridge and replace it. We were able to mount instruments on it, test it under various load conditions and even inflict damage just before it was demolished.
Question 10. A ten-year positive change for microwave device:
Answer: H
Supporting sentence: A commercial system based on the Los Alamos hardware is available, complete with the Stubbs algorithms. In a decade there is a possibility of a battery or solar-powered package mounted under each bridge, scanning it every day to detect changes.
Keywords: electronics, microwave, bridges
Keyword Location: 8th paragraph, 2nd line.
Explanation: As the electronics become cheaper, a microwave inspection system will eventually be applied to most large bridges in the US.
Question 11. The chance they get a honorable contract:
Answer: G
Supporting sentence: When any structure is vibrating, the energy is divided throughout with some points not in motion, while others vibrate strongly at different frequencies,” says Stubbs. His algorithms use pattern recognition to detect changes in the distribution of this energy.
Keywords: NASA, frequency, algorithms, energy, space shuttle
Keyword Location: 7th paragraph, last line.
Explanation: NASA already uses Stubbs’ method to check the behaviour of the body flap that slows space shuttles down after they land.
Question 12. Explanation of the mechanism for the new microwave monitoring to work:
Answer: B
Supporting sentence: By monitoring these movements with the device which uses a microwave to measure distance for a few minutes, the researchers can find out how the bridge resonates. Changes in its pattern can give an early warning of damage.
Keywords: traffic, distance, bridge, microwave.
Keyword Location: 2nd paragraph, 2nd line
Explanation: Any load on the bridge – such as traffic induced displacements, which change that distance as the bridge moves up and down.
Question 13. how is the damage deliberately created by the researchers
Answer: E
Supporting sentence: The Engineers created damage that they hoped would simulate fatigue cracks that can occur in steel girders.
Keywords: Steel girders, flange.
Keyword Location: 5th paragraph, 2nd line
Explanation: The engineers first cut a slot about 60 cm long in the middle of one girder. They then extend the cut until it reaches the bottom of the girder and finally they cut across the flange.
Also Check: FAIR GAMES IELTS Reading Passage with Answers







